Departments are organizational units within a company that are responsible for specific functions or tasks. In the context of the ERP software, departments could include such as: administration, sales, marketing, finance, human resources, and operations. In ALZERP cloud ERP software, each department may have its own set of responsibilities, goals, and workflows.
ALZERP offers a pre-configured set of departments and associated management types, employee sections and operational executions teams which seems to be focused on roles commonly found in wholesale and distribution businesses. Here’s a possible breakdown of the listed departments and management types:
- ADMINISTRATORS: This likely represents the highest access level with full control over the entire ERP system, managing users, departments, and configurations.
- BRANCH ADMIN: This role might have full access to manage data and functionalities specific to a particular branch location.
- PURCHASE OFFICER: This user type would likely have access to functionalities related to purchasing inventory, managing suppliers, and potentially approving purchase orders.
- STORE OFFICER: This role might be responsible for managing inventory levels, stock movements within the warehouse, and potentially picking and packing orders.
- SALES OFFICER: This user type would likely have access to functionalities related to creating sales orders, managing customer accounts, and potentially generating invoices.
Employee Access Levels based on Management Types:
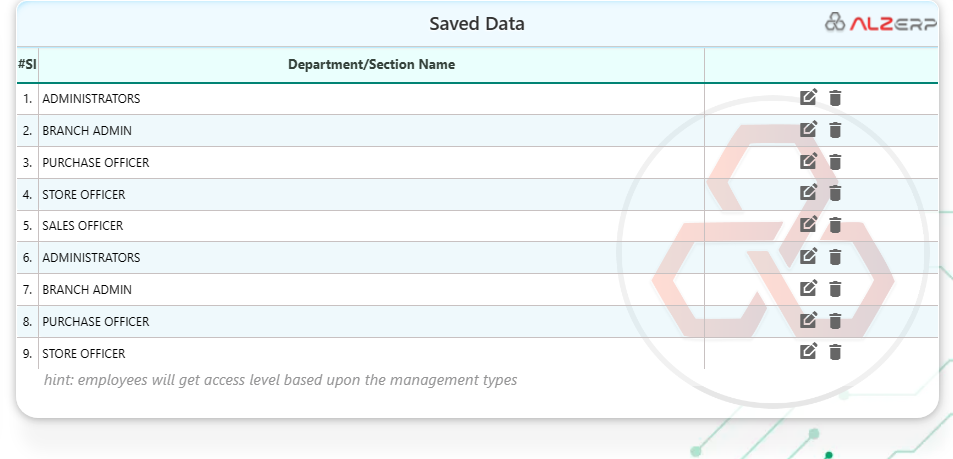
As the hint suggests, when you assign employees to these departments and specific management types within ALZERP, their access levels within the ERP system are automatically determined. This ensures:
- Simplified User Management: Pre-defined roles streamline the process of assigning permissions.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Users only have access to the functionalities they need to perform their jobs effectively, enhancing data security.
- Improved Efficiency: Users can focus on their tasks without needing access to irrelevant information.
Department and Access Control Management:
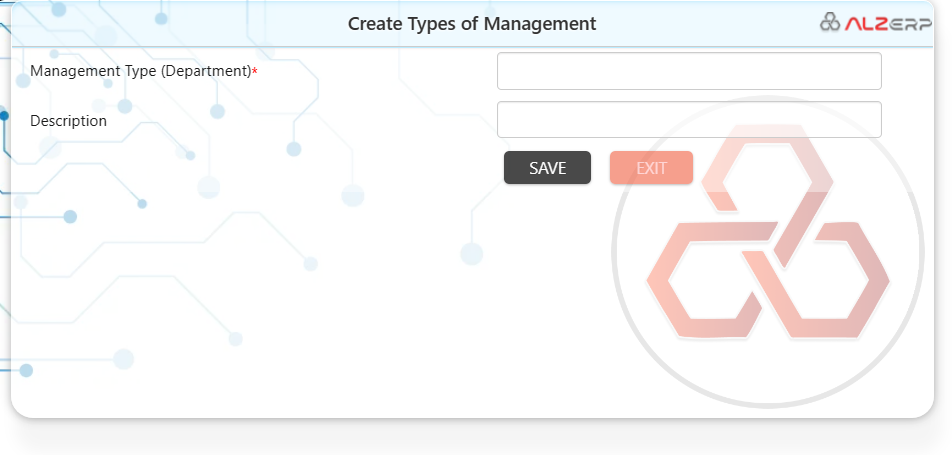
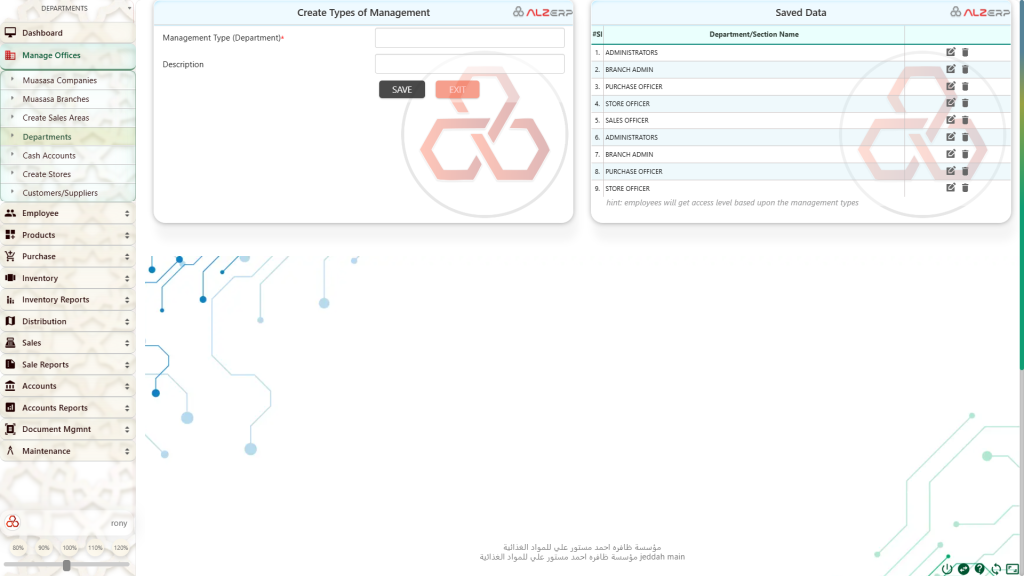
This module allows you to define the organizational structure of your company and manage user permissions within the ERP system.
- Departments in a Company: Create a hierarchical structure to represent your company’s departments (e.g., Sales, Marketing, Finance, Human Resources).
- Create Types of Management (Management Type (Department)*): Here you can define different management levels or access groups within each department. These might be:
- Executive (Full access to departmental data and functionalities)
- Manager (Manages departmental activities and has some access restrictions)
- Team Member (Limited access based on specific job roles)
- Description: Provide a brief description for each management level, clarifying the associated permissions and responsibilities.
- Saved Data (#Sl, Department/Section Name): This section likely displays a table with the following information:
- #Sl: Sequential number for easy reference.
- Department/Section Name: The name of the department or sub-section within the department hierarchy.
Access Control based on Management Types:
The key takeaway here is that user access levels within the ERP system will be determined by the department someone belongs to and the specific management type assigned to them. This ensures:
- Data Security: Only authorized users have access to relevant data based on their job roles and departmental needs.
- Improved Efficiency: Users have the tools and information they need to perform their tasks effectively.
- Reduced Risk: Limits the potential for unauthorized access to sensitive information.
This feature allows administrators or authorized users to define different types of management roles or hierarchies within the organization. These management types could represent various levels of authority, responsibility, and access privileges within the ERP system.
For example, management types could include roles such as administrators, branch administrators, purchase officers, store officers, and sales officers, as listed in the provided example.
Each management type may have specific access levels and permissions granted within the ERP software. Access levels determine the features, data, and functionalities that users belonging to each management type can access and manipulate.
The hint provided suggests that employees’ access levels within the ERP software are determined based on the management types assigned to them. This implies that employees are granted access to relevant modules, functions, and data based on their roles and responsibilities within the organization.
For instance, administrators may have full access to all modules and functionalities of the ERP system, while branch administrators may have restricted access limited to their respective branches. Similarly, purchase officers may have access to procurement-related modules, store officers to inventory management modules, and sales officers to sales and customer management modules.
By defining and assigning management types, organizations can effectively control access to sensitive data, ensure compliance with security policies, and streamline business processes within the ERP software.
Let’s explore the features related to departments and management types in an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software:
- Integration:
- ERP systems eliminate data silos by providing a central view of essential financial, operational, and business data.
- Data can be shared across the organization in near-real-time, fostering efficiency and collaboration.
- Automation:
- ERP automates repeatable tasks such as payroll, order processing, invoicing, and reporting.
- This minimizes manual data entry, reduces errors, and allows employees to focus on value-added activities.
- Data Analysis:
- Effective data analysis is crucial for optimizing operations, reducing costs, and identifying new business opportunities.
- ERP systems empower employees to gather diverse information and turn it into actionable insights.
- Inventory Management:
- ERP helps manage inventory efficiently by tracking stock levels, reorder points, and supply chain processes.
- It ensures timely replenishment and minimizes stockouts or overstock situations.
- Order and Supply Chain Management:
- ERP streamlines order processing, from creation to fulfillment.
- It integrates supply chain functions, enhancing visibility and coordination.
- Procurement and Production:
- ERP facilitates procurement by managing vendor relationships, purchase orders, and supplier performance.
- It optimizes production processes, ensuring timely manufacturing and delivery.
- Distribution and Fulfillment:
- ERP handles distribution logistics, including warehouse management, shipping, and delivery.
- It ensures accurate order fulfillment and customer satisfaction.
- Human Resource Management (HRMS):
- ERP modules for HR manage employee data, payroll, benefits, and performance.
- Access levels are assigned based on management types, ensuring data security.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
- Some ERP systems include CRM capabilities for managing customer interactions, sales, and marketing.
- CRM data can inform decision-making and improve customer service.
- E-commerce Integration:
- ERP systems with e-commerce features enable online sales, inventory synchronization, and customer order tracking.
- Seamless integration enhances customer experience and business growth.
- Financial Reporting:
- ERP provides accurate financial data for reporting, compliance, and decision-making.
- It generates financial statements, balance sheets, and income statements.
- Business Intelligence (BI):
- ERP systems turn data into actionable insights through analytics and reporting.
- BI tools help allocate resources effectively and identify market opportunities.
Remember that ERP systems vary, and organizations can customize features based on their specific needs. By using this Department and Access Control module, you can establish a secure and efficient user management system within your ERP software, ensuring data security and optimized workflows across your organization.